How artificial intelligence is changing health care
Artificial Intelligence is here, and it has already altered the fundamental fabric of everyday human experience. The integration of AI into modern medicine represents a transformative shift for the first time in decades. The application of AI in healthcare completely changes our perspective on how patients are diagnosed, treated, and evaluated, providing better, faster, and more efficient care. It has transformed traditional healthcare practices, starting from administrative work to patient treatment. Due to its ability to process vast amounts of clinical data faster and accurately. many countries are now shifting towards use of AI in medicine.
The impact of AI in healthcare is extensive, influencing everything from hospital administration and data management to diagnosis and clinical decision-making. AI takes over the time-consuming, low-level tasks, freeing up humans for more critical work. Experts anticipate continued growth in AI adoption within healthcare, leading to significant breakthroughs, early disease detection, and the possibility of discovering cures.
A Historical Perspective:
The use of AI in healthcare is not a new concept. It has been there since the 1970s with INTERNIST-1. INTERNIST-1 is the world’s first artificial medical consultant. It used a series of algorithms to help in reaching a diagnosis for the patient. Significant advancements in AI began in the early 2000s with the introduction of systems like Watson and Pharm Bot. In 2017, the Watson system was introduced that was successfully able to identify RNA-binding proteins linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Pharm Bot, developed in 2015, was used for educational purposes for medicine.
Key application of AI in healthcare:
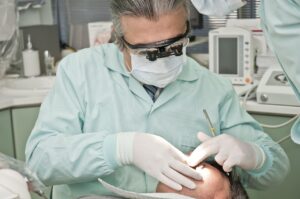
Medical Imaging and Diagnostics:
The integration of artificial intelligence into medical imaging has substantially advanced clinical practice by facilitating early disease detection, improving diagnostic accuracy, and generating highly detailed and precise visualizations of the human anatomy. By using advanced algorithms and machine learning, AI minimizes labor-intensive tasks such as enhancing image quality for more accurate diagnoses, accelerating diagnostic processes, and performing precise image segmentation. Utilizing machine learning algorithms, AI analyzes medical results and imaging with exceptional speed, precision, and depth. X-ray imaging, CT scans, positron emission tomography (PET) and MRI technologies serve as prominent examples of artificial intelligence applications in healthcare. By using previous datasets, artificial intelligence can identify underlying abnormalities in advance that might otherwise go unidentified by the human eye.
Drug discovery and development:
The adoption of artificial intelligence has significantly expanded within the pharmaceutical industry, particularly in advancing digitalization efforts. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data and predict future outcomes supports various stages of drug development, including disease-specific drug design, compound formulation, and optimization of drug structures. Artificial intelligence, through the use of machine learning and deep learning algorithms, facilitates the identification of neoantigens that are crucial for the development of cancer vaccines. Ongoing research focuses on the discovery of novel molecules and simulations aimed at achieving specific pharmaceutical objectives. Companies such as Roche are actively exploring and implementing innovative AI-driven approaches to accelerate drug discovery and development.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine refers to the customization of medical treatment for an individual patient based on their unique molecular, physiological, ecological, and behavioral characteristics. Artificial intelligence has increasingly been integrated into this field, challenging the traditional ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to healthcare. By employing advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques, AI analyzes a wide range of patient-specific data to support accurate diagnoses and develop tailored treatment plans. Furthermore, AI can predict a patient’s response to specific drugs and proposed therapies, enabling real-time adjustments to optimize clinical outcomes. Artificial intelligence in personalized medicine has contributed significantly to the early detection of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and various cardiovascular disorders. In certain cases, AI has even demonstrated the ability to predict the onset of these diseases before clinical symptoms appear.
Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots
Chatbots and virtual assistants have streamlined access to healthcare information, enabling users to receive prompt solutions to their concerns. These AI-driven tools are rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape by combining artificial intelligence with human input to deliver intelligent diagnostic support, mental health guidance, and management of minor, non-critical conditions—such as the common cold or mild fever—without requiring a visit to a healthcare facility. These chatbots are particularly beneficial for hospitals with limited administrative staff, as they enable patients to schedule appointments online efficiently and with minimal risk of error. Rather than navigating through extensive online content in an attempt to self-diagnose, chatbots efficiently deliver only the most relevant information necessary for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By reducing costs, saving time, and enhancing diagnostic precision, the use of AI-powered virtual assistants is anticipated to experience substantial growth by 2030. Notable companies leading innovation in this space include Wombat Labs, Densely Inc., Ada Digital Health Ltd., Babylon Health, and Buoy Health Inc.
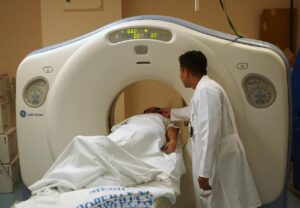
Emergency support and Robotic Surgery:
AI-assisted robots have increasingly been integrated into emergency rooms and operating theaters. Robot-assisted surgeries are emerging as a significant advancement in modern medicine, offering enhanced precision, greater control, and improved surgical outcomes. These robotic procedures are particularly effective in accessing deep anatomical regions, often utilizing small incisions to insert cameras and surgical instruments.
A prominent example of robot-assisted surgery is the da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, CA), which enables surgeons to perform complex procedures with high precision through a robotic interface. In this system, the surgeon operates from a console, executing detailed hand movements that are replicated in real-time by robotic arms on the patient positioned on the operating table. It is important to note that the da Vinci system functions entirely under human control and cannot operate autonomously.
Another notable example is the Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR), which specializes in soft tissue reconstruction. STAR employs advanced imaging and AI to analyze the damaged area and autonomously perform precise suturing. Beyond soft tissue repair, robotic technologies like STAR are also applied in bone carving, reconstruction, and drilling, as well as in blood sample collection and radio surgical procedures for brain and spinal malignancies—all conducted under strict human supervision.
Administrative Workflow Automation

Artificial intelligence has significantly enhanced administrative operations within the healthcare sector by automating routine tasks, minimizing paperwork, and eliminating errors in scheduling medical staff. By streamlining workflows and reducing administrative bottlenecks, AI helps to improve overall efficiency and reduce the risk of human error, thereby contributing to more accurate outcomes. Studies indicate that the implementation of AI for administrative purposes has led to notable reductions in both operational costs and time, ultimately improving the quality of patient care. AI-driven systems can identify patients requiring urgent attention, auto-fill medical records using historical patient data, and help mitigate potential legal issues. Additionally, patients can schedule appointments online, receive assistance with prescriptions and medication management, and avoid issues such as double-booking. These systems also support financial management within healthcare institutions by efficiently overseeing billing, accounts, and related administrative tasks.
Really a good blog. it is best of all.
Trending topic, and very usefull information
Ai is helping modern world, but it should be used with proper care and precautions.
Everything is very informative and well written.